Have a question about Tesla that you'd like answered? Submit it using the TWP Application Form.
Question: I'm an artist and inventor. I've seen the Tesla coils in Boston and I was thinking, has anyone ever put an electric magnet field over a Tesla coil and has anyone made improvements on
it?
Answer: Being coils of wire, both the Tesla coil primary and the secondary are by definition electromagnets.
They are both surrounded with pulsating magnetic field lines when the Tesla coil
is in operation. In operation, a pulsating electric field is also
associated with these devices. As for improvements, the Tesla coils that you saw in Boston are most likely disruptive discharge type oscillators.
This means that there is some sort of a spark gap circuit controller in series with a high-voltage capacitor in the primary circuit.

Both the vacuum-tube Tesla coil and the solid-state Tesla coil can be viewed as an improvement over the disruptive-discharge Tesla coil. Tesla himself improved upon the classic Tesla coil by replacing the spark gap and capacitor with a specially-designed electrical alternator. He also tightened the coupling of the primary and secondary windings, and then added a third coil called the "extra coil." This resulted in a Tesla-coil design that is known as the "magnifying transmitter."
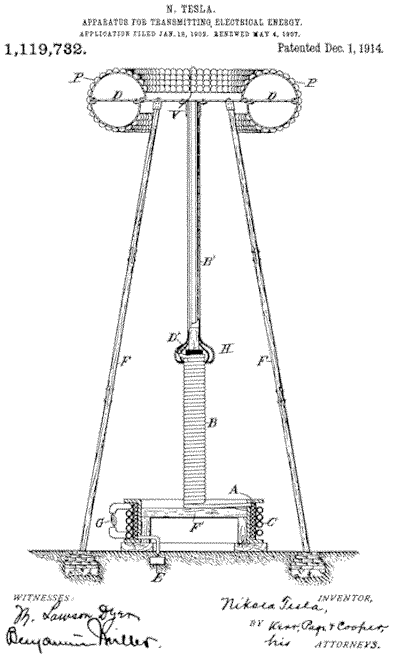
An approximate drawing of the magnifying transmitter that Tesla almost finished building at Wardenclyffe.
There are two types of wireless transmitter that can be built using an improved Tesla coil. The first is quite similar to the classic Tesla coil that you saw in Boston, the main difference being the placement of the upper terminal or topload. Instead of mounting it close-in just above the helical resonator's top turn, the topload is elevated somewhat above the top turn. This type of transmitter requires that a precisely tuned helical resonator type receiver be set in place in order for it to function. That's why in the related wireless patents Tesla almost always shows both the transmitter and the receiver as shown below.

In the case of this type transmitter, the transfer of electrical energy is between the two ground terminals in the form of true conduction currents, and also between the elevated terminals.
In a low power system, the transfer of energy between the elevated terminals is, in effect, the result of displacement currents, much like the transfer of electrical energy which takes place between the plates of a capacitor in an AC circuit.
This might be called the type-one transmitter.
The second of the Tesla-type transmitters consists of a type-one transmitter plus an unloaded helical resonator receiver, both placed in close proximity to each other, each with an independent ground connection. Tesla first illustrates
this improved type-two transmitter in his Colorado Springs laboratory notes.

The following illustration shows a type-two transmitter in operation. A receiver is standing off to the right.

In operation, a powerful current flows through the earth between the two ground terminals. The coupling between the transmitter's two elevated terminals is by electrostatic induction or, in the case of a high-power transmitter, by true electrical conduction through plasma. There is also some degree of inductive magnetic coupling between the two resonators. The type-two transmitter is particularly well suited for the excitation of earth resonance modes. It's interesting to see that in the related patent, ART OF TRANSMITTING ELECTRICAL ENERGY THROUGH THE NATURAL MEDIUMS, Tesla shows a form of receiver that does not involve a resonator coil.
Question - I want to know why it is that no one ever took the task of verifying whether Tesla’s idea of Global communication actually works. Where can I see some technical details about this system, with diagrams, etc.? What exactly was the mechanism of the Wardenclyffe station and how would it work? The more I read, the more I feel that concerning the handling of large amounts of electricity we are still living in the ancient ages. Electronics has advanced so much, while we still use power lines to transmit power, losing millions of dollars in generation and transmission costs. It would be amazing if it were possible to do away with these losses.
Thanks for contacting the Tesla Wardenclyffe Project regarding Nikola Tesla's engineering legacy and his plan for a system of global wireless telecommunications. While achieving earth resonance and validating the World System concept would be an expensive undertaking, it is possible this has already been done. Such investigations would be best accomplished with what might be called a type-two transmitter, such as developed by Tesla in 1899 at the Colorado Springs experimental station. This circuit consists of two separate elements, a grounded alternator-driven continuous-wave oscillator and an adjacent grounded free oscillatory system, both installed in relatively close proximity to each other. As for the availability of technical documentation, nothing truly substantial has been published yet in the open literature.
Actually it quite easy to reproduce some of Tesla's results on a small scale. The basic setup consists of a non-sparking Tesla coil with a slightly elevated capacitance for the transmitter, and an identically tuned helical resonator with an elevated capacitance for the receiver. The influence of the Tesla transmitter is seen by observing the local electric or magnetic fields developed in the close vicinity of the receiving apparatus. While this second arrangement does not involve earth resonance and the establishment of terrestrial standing waves, it does demonstrate the connection of a type-one Tesla transmitter to a passive Tesla receiver by true conduction currents flowing through the ground and the action of what might be called displacement currents between the two elevated conducting bodies. As for technical details and diagrams, etc., there are a number of primary sources. To start with, here are some of the principle patents more or less associated with the World System:
Tesla developed two slightly different methods for the wireless transmission of electrical energy. These were what might be called 1) atmospheric conduction and 2) earth resonance. Both of these involve the development of electrical currents flowing in the earth using a powerful magnifying transmitter. In 1932 journalist J.J. O’Neill conducted an interview with Tesla in which he makes a distinction between the two.
I also asked him if he is still at work on the project which he inaugurated in the '90's of transmitting power wirelessly anywhere on earth. He is at work on it, he said, and it could be put into operation. . . . He at that time announced two principles which could be used in this project. In one the ionizing of the upper air would make it as good a conductor of electricity as a metal [using a very powerful type-one transmitter]. In the other the power would be transmitted by creating "standing waves" in the earth by charging the earth with a giant electrical oscillator [of the type-two design] that would make the earth vibrate electrically in the same way a bell vibrates mechanically when it is struck with a hammer. "I do not use the plan involving the conductivity of the upper strata of the air," he said, "but I use the conductivity of the earth itself, and in this I need no wires to send electrical energy to any part of the globe." [Tesla Cosmic Ray Motor May Transmit Power 'Round Earth Brooklyn Eagle, July 10, 1932, John J. A. O'Neill]
See the series of Q&A's starting at http://www.tfcbooks.com/teslafaq/q&a_046.htm for some additional thoughts on this subject. Regarding Tesla wireless theory, I suggest the book Nikola Tesla On His Work With Alternating Currents and Their Application to Wireless Telegraphy, Telephony, and Transmission of Power as a starting point. This book is available through inter-library loan. Additionally, you might look into the writings of James and Kenneth Corum, keeping in mind that theirs is still a work in progress and subject to revision as the science becomes further developed.
Question - I am doing a research project and am trying to find out if Mr. Tesla's Ionization device created by some sort of high frequency waves, was ever sold here in the U.S.A. My research tells me that a device was at one time sold for scalp massages and also used in the beauty industry for facial cleansing and other oxidization of the skin. I would be very grateful for any assistance you can give me or any sources that you may be able to suggest.
It sounds like you are referring to the the violet ray device. This is an electrical appliance intended for the physical application of high potential, high frequency electrical current for electrotherapeutic purposes. It consists of two basic elements, a Tesla coil transformer assembly and a gas filled electrode. These instruments were very popular in the early part of the 20th century and were widely marketed. While the efficacy of the device has been called into question, it is said to work by stimulating blood circulation. See Violet Ray Generators for some additional information and further links.
Previous Questions and Answers:
Question 1 - I am currently investigating for a film documentary on the subject of lost and hidden inventions. I believe Nikola Tesla is one suitable to reference. However there is one thing I don't understand, if it is so easy to build a Tesla engine why don't we all have one in our homes. Please help. I understand how and why it works. I do not understand why the Tesla engine is not more widely available and in use. - 2/8/99This question is not easily answered. The basic bladeless turbo-machinery design has been around for about 90 years, in the form of both a pump and an engine. In spite of this the Tesla pump was not commercialized until the 1980's. These devices are now generating sales in the millions of dollars annually, being acknowledged as the best pump for certain special applications such as pumping highly corrosive fluids.
The Tesla turbine is presently in the same position as was the pump in the late 1970's. Up to 1995 it appears that no true Tesla turbines were actually constructed — since Tesla himself that is. Modern-day replicas of Tesla's disk turbine have now been run on steam and with very limited success using direct combustion.
There is now serious commercial interest in Tesla's engine, and they may yet become available, just as occurred with the pumps after they were demonstrated to work in the early 1980's and embraced by the petrochemical industry. Texaco claimed in 1986 they were saving $68,000 per year per pump, this from a device publicly demonstrated, though unappreciated, since 1911. While he appears to have developed a functioning gas turbine, Tesla himself had insurmountable difficulties when it came to the introduction of a commercially viable version. There are some who believe the fundamental turbine design will see greater utilization in the future based upon its durability under adverse operating conditions. Other factors leading in this direction are the inherent simplicity of the disk-type rotor, and recent advances in materials technology. [revised 05/23/2003]
Regarding Tesla's style of invention, it has been my general observation that he approached every problem in a highly systematic manner. Naturally, the very first thing was identification of the problem. In the case of more complex problems, it appears he would engage in a detailed mental analysis in which he would break down the possible solutions that came to him into discrete steps. At this point he would start building the devices that he had created in his mind.
In some cases his creations were extensions of existing devices and concepts, with his own original ideas thrown into the pot, so to speak. In other words, he stood on the shoulders other inventors who had come before him. An example of this is the AC induction motor in which he was able to eliminate the brushes and commutator, common to all the existing electric motors of the time. He did this by using the principle of electromagnetic induction that had already been embodied in the electrical transformer. It was his own genius that came up with the idea of using alternating currents generated in multiple phases (he called it the poly-phase system) to produce a rotating magnetic field within the motor's stator windings. That made the whole idea come together.
Another example is the four tuned circuit configuration for wireless communications — the system we now know as radio. One of the earliest devices for producing weak radio frequency waves consisted of a common induction coil with two metallic spheres connected to its secondary terminals, in the form of a spark gap. Along with two metallic plates they created an energy storage device of small capacity that was charged by the coil and periodically discharged through the gap. Tesla had the idea of moving this condenser to the primary side of the coil where it could be of much greater storage capacity and also form part of a resonant primary circuit. With the addition of an elevated antenna and a ground connection (these were also Tesla's original ideas) and a few years worth of refinements, he had produced a powerful radio transmitter.
These are only a couple of examples of Tesla making significant improvements and adaptations based on earlier designs. As Tesla's career took off, in many cases these improvements and adaptations stemmed from earlier designs of his own creation. A good example of such an evolution is found in Tesla's mechanical and electrical oscillator which started out as a simple experimental device for the production of mechanical vibrations. This device was modified over time to serve a number of different functions related to Tesla's wireless investigations. The machine also saw use for the generation of electricity, possibly as a power source for lighted navigation buoys. In his later years Tesla proposed a system for geophysical prospecting using a variation of this device called the telegeodynamic oscillator.
In regards to additional sources of information, I especially recommend the book Nikola Tesla On His Work With Alternating Currents and Their Application to Wireless Telegraphy, Telephony and Transmission of Power, edited by Leland Anderson. It should give you a better idea of the workings of Tesla's mind, especially as they pertain to the development his wireless system.
I believe the Tesla "Water Pump" to which you refer is indeed the Tesla disk pump that was described in his 1913 U.S. Patent titled FLUID PROPULSION, No. 1,061,142. This rotary pump consists of shaft-mounted disks suspended on bearings within a cylindrical casing — a design which is essentially the same as that of the disk turbine. In operation, a fluid which is admitted by way of ports at the center of the disks is forced to flow between them in free spiral paths to be expelled through an outlet extending from the casing's periphery. The motor-driven disks are able to impart their energy to the more or less viscous fluid primarily because of the fluid's adhesion to the faces' of the disks.
I should mention that while Tesla's pump does great job moving plain water, the real value of this invention is its use in extreme pumping applications. The fact that it is not subject to internal damage from impingement or cavitations makes it perfect for pumping boiling water, fluid-suspended solids, and highly corrosive fluids. One final note, a few years ago someone built a prototype automotive water pump that consisted of a disk pump driven by a 12 volt DC electric motor. Perhaps this is the device that you heard about.
In 1916 while describing his early experiments in wireless, Tesla spoke about the distances between the transmitting and receiving stations saying,
"The distance at that time, and I think the greatest distance at which I ever received signals from the Houston Street laboratory, was from the Houston laboratory to West Point. That is, I think, a distance of about 30 miles. This was prior to 1897 when Lord Kelvin came to my laboratory. . . . In that experiment I produced continuous trains of oscillations and went with the instrument to West Point. I did this two or three times. There were no signals actually given. I simply got the note, but that was for me just the same."
I am unaware of any verifiable account of Tesla ever having transmitted the sound of a human voice.
Tesla's career in electrical engineering began with a good education. He got this by auditing courses at the Austrian Polytechnic School in Graz and the University of Prague. His first job as an engineer was with the Yugoslavian government, assisting with the initial installation of that countries telephone system. The great value of such on-the-job training shouldn't be ignored. In 1883, Tesla worked for one year at Thomas Edison's European subsidiary in Paris, after that he traveled to New York where he worked for Edison directly.
As for his youth, I suggest that you borrow a copy of Tesla's autobiography for a first hand story. If your Public Library doesn't have it, ask the librarian if they can get a copy via Intra-Library Loan (ILL). While your at it, you should read the excellent Tesla biography entitled Tesla — Man Out of Time. This will give you a background on the entire life of this visionary inventor.
Thanks for your interest in Nikola Tesla. Please let us know if you need any further assistance.
The engine you heard about is an invention called the Tesla disk turbine. Tesla's engine is simple in construction, consisting merely of shaft-mounted heat resistant disks that are placed within a cylindrical casing. In operation, high velocity gas is introduced tangentially at the periphery of the disks to flow between them in free spiral paths and exit through central exhaust ports. The slight viscosity of the propelling gas along with its adhesion to the faces of the disks combine to efficiently transfer the fuel's energy to the disks and on to the shaft. A major advantage which the Tesla turbine has over conventional turbines, and piston engines as well, is its relative simplicity of construction.
One important way to improve any turbine's performance to increase turbine inlet temperature. For every 350 degree Fahrenheit increase in turbine inlet temperature, the horse-power output of a given size turbine engine will double, without any increase in size and weight. Also the fuel efficiency will increase from 10% to 11% for each 350 degree F. of turbine inlet temperature increase. The high power-to-weight ratio that you mentioned might be achieved by a Tesla turbine if it were constructed out of a ceramic composite or some other exotic material that can resist the extremely high temperatures that result from the combustion of a fuel such as gasoline at the correct stochiometric fuel/air ratio. For fossil fuels, this temperature is about 3500 degrees Fahrenheit, which, in operation, is sufficiently high to soften any one of the presently available construction materials and subject an engine's rotor to stress related failure. A related factor is the basic symmetry of the Tesla turbine rotor disks allowing them to resist failure by eliminating the possibility of combined bending stresses that all conventional turbine blades experience.
So, you can see that while Tesla's bladeless turbine even now has the
potential to out perform temperature limited bladed turbines, materials
technology has not yet reached the point where truly optimal performance can be
obtained.
It was the Tesla Wardenclyffe Project's partner group in on Long Island, the Friends of Science East, that sponsored the earlier lecture series to which you refer. And, I am sure that additional Tesla related lectures will be scheduled in the future.
Please keep an eye on the TWP website for advance notice of any future
events.
The Tesla Engine Builders Association answers: Not that we know
of. Real Tesla turbines are still a very rare breed. [Try contacting TEBA directly at
teba@execpc.com and ask if the
organization has any members in New York or the outlying suburbs, even if they
are not active builders. Ask TEBA to forward your request to them along
with your contact information. Perhaps you can get something up and
running there in Nikola Tesla's home town, even if there are is no activity at
the present time. 12/14/98]
Tesla had at least four labs in Manhattan. The earliest was located at 89 Liberty Street, followed by one at 175 Grand Street. The third, the 35 South 5th Avenue lab, was destroyed by fire in 1895. The fourth, which you mentioned in your e-mail, was at 46 Houston Street. It was at his second lab in 1898 where the efficient magnifier Tesla coil configuration was first demonstrated. A fifth lab is said to have been located under the 59th Street Bridge near 2nd Avenue in the 1930s.
In regards to their condition, the building at South 5th Avenue has probably
been replaced. I'm not aware of the condition of the Houston St. structure
or even if the original building is still standing. As for the supposed
lab at 59th & 2nd, who knows?
Prior to 1942, how big was a multi decade resistance box of the type used for Wheatstone Bridge resistance measurements? What did it look like? I am referring of course, to the device that was mysteriously enclosed in a box and kept in the vault of the Governor Clinton Hotel in New York. - 12/7/98
I can't give you specific figures as to the typical dimensions of a pre-1942 decade resistance box. A few years back I happened to see one that could have been from the 30s or 40s that was about 14" x 7" x 5" in size. Please keep in mind that these figures are very rough estimates based solely on my recollection--no measurements were taken. The instrument that I saw consisted of what appeared to be a Bakelite box with a top containing a number of multi-position rotary switches and probably one or more rheostats, much the same as present day decade resistance boxes. The introduction of carbon resistors accounts for the considerable reduction in size of our modern instruments. In Tesla's time electrical resistors were created by winding on to a spool a piece of insulated resistance wire of a length that would give the desired resistance. In manufacturing these wire wound resistors, bifilar windings were often incorporated thus creating an anti-inductive resistor which could be used in radio work. One application of the anti-inductive resistor was for setting the dc bias voltage which was placed across the nickel chip coherers which Tesla used in his wireless receivers.
A good source of information on antique electrical instruments is the New
Wireless Pioneers, Box 398, Elma, NY 14059, a supplier of vintage radio
books. They carry titles covering a number of different subjects such as
Amateur radio, Broadcasting 1929-30, Biographies of famous inventors and
scientists, Bibliographies, Broadcasting, Computers, Electricity, Light bulbs,
Motors/dynamos, Phonographs, Post 1930 radio, Physics, Radar, Sound/audio,
Telephones, Telegraphy, Transistors, Tesla and high voltage, Television, Vacuum
tubes, wireless books before 1920 and X-rays. To receive their catalog
write to: wireless@pce.net.
While to the best of my knowledge Tesla did not manufacture any radio sets
for commercial purposes, the Lowenstein Radio Company did manufacture a 5,000
watt quenched-spark transmitter licensed under Nikola Tesla Company
patents. These transmitters were installed on naval vessels prior to WWI
and adopted the flat spiral antenna circuit coil shown in Tesla's wireless
patents No. 645,576 and 649,621 issued in May 1900. One of these
transmitters can be seen in the Nikola Tesla Photograph Archives section.
As you probably know, in 1899 Nikola Tesla spent some time in Colorado Springs. He was there to work out some design details for the wireless communications facility that he would later start to build on the North Shore of
Long Island, New York. In 1917 during a speech before the American Institute of
Electrical Engineers Tesla said that while in C/S his large oscillator once
created a dense cloud of water vapor inside of the laboratory building. He
also speculated that properly designed plants might be installed in arid regions
to draw in water for irrigation. The story that you heard is probably
related to this incident. By the way, the entire speech is reprinted in
the book TESLA SAID. See page 188 for the specific account.
Here are some paragraphs adapted from a paper about Wardenclyffe that should answer many of your questions.
From: A MUSEUM AT WARDENCLYFFE - THE CREATION OF A MONUMENT TO NIKOLA TESLA
The year was 1900 and following 9 productive months of wireless propagation research in Colorado, Nikola Tesla was anxious to put a mass of new found knowledge to work. His vision focused on the development of a prototype wireless communications station and research facility and he needed a site on which to build. In 1901 he cast his eyes some 60 miles eastward to the north shore village of Woodville Landing. Only six years before the north branch of the Long Island Railroad had opened, reducing travel time to the locality from a horse drawn five hours to less than two. Seeing an opportunity in land development a western lawyer and banker by the name of James S. Warden had purchased 1400 acres in the area and started building an exclusive summer resort community known as Wardenclyffe-On-Sound. With an opportunity for further development in mind, Warden offered Tesla a 200 acre section of this parcel lying directly to the south of the newly laid track. It was anticipated that implementation of Tesla's system would eventually lead to the establishment of a "Radio City" to house the thousands of employees needed for operation of the facility. The proximity to Manhattan and the fairly short travel time between the two, along with the site's closeness to a railway line must surely have been attractive features and Tesla accepted the offer.
The Wardenclyffe World Wireless facility as envisioned by Tesla was to have been quite different from present day radio broadcasting stations. While there was to be a great similarity in the apparatus employed, the method in which it was to be utilized would have been radically different. Conventional transmitters are designed so as to maximize the amount of power radiated from the antenna structure. Such equipment must process tremendous amounts of power in order to counteract the loss in field strength encountered as the signal radiates out from its point of origin. The transmitter at Wardenclyffe was being configured so as to minimize the radiated power. The energy of Tesla's steam driven Westinghouse 200 kW alternator was to be channeled instead into an extensive underground radial structure of iron pipe installed 120 feet beneath the tower's base. This was to be accomplished by superposing an extremely low frequency (ELF) signal on the higher frequency signal coursing through the transmitter's helical resonator. The low frequency current in the presence of an enveloping corona-induced plasma of free charge carriers would have pumped the earth's charge. It is believed the resulting ground current and its associated wave complex would have allowed the propagation of wireless transmissions to any distance on the earth's surface with as little as 5% loss due to radiation. The terrestrial transmission line modes so excited would have supported a system with the following technical capabilities:
The plan was to build the first of many installations to be located near major population centers around the world. If the program had moved forward without interruption, the Long Island prototype would have been followed by additional units, the first of which being built somewhere along the southwest coast of England, perhaps in Cornwall. By the Summer of 1902 Tesla had shifted his laboratory operations from the Houston Street Laboratory to the rural Long Island setting and work began in earnest on development of the station and furthering of the propagation research. Construction had been made possible largely through the backing of financier J. Pierpont Morgan who had offered Tesla $150,000 towards the end of 1900. By July 1904, however, this support had run out and with a subsequent major down turn in the financial markets Tesla was compelled to pursue alternative methods of financing. With funds raised through an unrecorded mortgage against the property, additional venture capital, and the sale of X-ray tube power supplies to the medical profession he was able to make ends meet for another couple of years. In spite of valiant efforts to maintain the operation, income dwindled and his employees were eventually dropped from the payroll. Still, Tesla was certain that his wireless system would yield handsome rewards if it could only be set into operation and so the work continued as he was able. A second mortgage in 1908 acquired again from the Waldorf-Astoria proprietor George C. Boldt allowed some additional bills to be paid, but debt continued to mount and between 1912 and 1915 Tesla's financial condition disintegrated. The loss of ability to make additional payments was accompanied by the collapse of his plan for high capacity trans-Atlantic wireless telecommunications. The property was foreclosed, Nikola Tesla honored the agreement with his debtor and title on the property was signed over to Mr. Boldt. The plant's abandonment sometime around 1911-1912 followed by demolition and salvaging of the tower in 1917 essentially brought an end to this era. Tesla's April 20, 1922 loss on appeal of the judgment completely closed the door to any further chance of his developing the site.
I recommend that you visit a local neon sign shop for your power supply transformer. You might also wish to contact the Tesla Coil Builders Association (TCBA) and ask about membership. [Editorial note: TCBA is no longer in business, but all back issues are available.] The address is:
Tesla Coil Builders Association
3 Amy Lane
Queensbury, NY 12804
Membership in the TCBA will put you in touch with a large community of people that have interests in common with your own. There you will find assistance with all of your TC building needs.
Say if a car [ignition] coil picked up a small piece of the power, would it not destroy the coil and the electrical system in the car? What about other thing such as TV's? Would this energy cause them to stop working and perhaps make the TV explode due to the power levels?
In effect would such a transmitter render all electronic equipment useless within the range of the coil ? Or would it be only things that are tuned into the 10 MHz that would be effected? - 3/4/98
The first thing to understand is that physical laws of propagation require that the World System operate at a fundamental frequency in the area below approximately 25 kHz. The following piece will help to clarify this statement:
REDISCOVERING THE ZENNECK SURFACE WAVE
In 1916 while speaking of his system for global transmission, Nikola Tesla cited the analysis of mathematician Arnold N. Sommerfeld as verification of his explanations of certain observed radio phenomena. Tesla was referring to his wireless communications system in which 90% to 95% of the electrical energy was manifested at the transmitter's output as "current waves" which were propagated through the ground by conduction, with the remainder being directed to the antenna structure, resulting in dissipating electromagnetic radiation. In 1909 another investigator by the name of Johann Zenneck, while working to explain Marconi's trans- oceanic results, showed that a unique type of surface wave could travel along the interface between the ground and the air. In the words of electrical engineer and noted Tesla researcher James Corum,
The distinguishing feature of the Zenneck wave was that the propagating energy didn't spread like radiation, but was concentrated near the guiding surface. Sommerfeld had shown that an electromagnetic wave could be guided along a wire of finite conductivity, and Zenneck conceived that the earth's surface would perform in a manner similar to a single conducting wire.
In commenting on Sommerfeld's analysis of the surface wave, Dr. James R. Wait states that "The field amplitude varies inversely as the square root of the horizontal distance from the source..." It is interesting to note that Sommerfeld made a point of distinguishing between the "electrodynamic" surface wave and its Hertzian counterpart the space wave, believing that both components could be present in varying proportion in the wave complex. It was Tesla's assertion that the exact composition of the emissions was dependant upon the design of the transmitter.
As the study of radio propagation progressed and certain mathematical analyses excluded it, some question as to the existence of Zenneck surface waves began to develop. In 1937 limited support was given to these doubts after tests showed simple antennas driven at 150 mHz produced 100 times lower field strength than predicted. More recent investigations show evidence that Zenneck waves can, indeed, be generated. The lower the frequency, the lower are the propagation losses. It is also apparent that they are not a major contributor to the field produced by an electric dipole or quarter wave radiator, however they can be strongly excited by a quarter wave helical resonator. Once again to quote Dr. Corum,
...the resulting wave is a surface guided (single conductor) transmission line mode which attenuates exponentially along the guide ...There is no inverse square spreading or diffraction, as with Hertzian waves...With appropriate constitutive parameters, a pure Zenneck wave would seem to hold out the promise of guided propagation with no radiation field to waste energy.
Plots of field strength vs. frequency indicate that a Zenneck wave propagates best at extremely low (ELF) and very low (VLF) frequencies and would loose much of its advantage as frequency rose above 1 mHz.
[The above piece is derived from Appendix II, "The Zenneck Surface Wave (A Fascinating Episode In the History of Radio Propagation)" of the paper entitled "Nikola Tesla, Lightning Observations and Stationary Waves" presented at the 1994 Colorado Springs Tesla Symposium.]
To answer to the next part of your question, you want to be aware that Tesla's World System was intended to provide both wireless global communications and power transmission. In fact, the first broadcast facility built at Wardenclyffe, New York was intended specifically for trans-Atlantic telephone communications. Plans were in the works for another similar facility to be built somewhere on the English coastline. In addition to the ELF radio-frequency signal, each transmitter would also generate multiple oscillations of higher frequency and all of these would be combined together to take the form of a wave complex extending, perhaps, up into the mHz area of the RF spectrum. In order for a receiver to pick up the desired portion of the signal it would need to be tuned simultaneously to two, three, or more of these oscillations. A system that was resonant with only one of the higher order vibrations of the wave complex would not respond. Assuming Tesla's World System were to be implemented at some time in the future, it is reasonable to anticipate that implementation of global radio and TV broadcasting would precede wireless electrical power transmission and that TV sets, and all other electronic equipment, would be redesigned accordingly.
By the way, there is no corroborating evidence that Tesla ever built an electric automobile, although he is known to have encouraged others to pursue the idea of electric propulsion. He defined this as the use of an engine to generate electricity which was transmitted to an electric motor used to turn a wheel or propeller, instead of turning them by direct mechanical means. If this sounds familiar you're right, as the idea has recently seen a revival by the automobile industry and others under the name "hybrid electric drive." The story of an electric Pierce Arrow that has been spread around appears to be a total fabrication.
The May 1919 issue talks about a "rotating brush wireless detector" that he used. Do you have any knowledge of either of these devices? I do not find them in the book of patents that I bought. - 2/26/98
Regarding Tesla's static eliminator, as you are finding out, there is relatively little info available about this device in the literature. It appears to be a variable coupling RF transformer consisting of two flat spiral or pancake coils. It looks like the upper coil could be raised up on the vertical column and locked in place at any desired position with set screws. In regards to the statement about the static eliminator having a patent, this might have been issued by a country other than the U.S.
Differing figures have been cited for the total number of patents obtained by Tesla worldwide. Based upon data found in the CATALOGUE OF TESLA PATENTS, Belgrade, 1987, and other sources [1,2,3], there were at least 236 patents issued to Tesla in 25 countries over the course of his lifetime. This figure breaks down as follows:
| Country |
Number of Patents Cataloged |
Actual Number Found * |
| Argentina | 1 | |
| Australia | 14 | |
| Austria | 4 | |
| Brazil | 2 | |
| Canada | 2 | 6 (+4) |
| Cuba | 1 | |
| Denmark | 1 | |
| Germany | 14 | 19 (+5) |
| Great Britain | 16 | 22 (+6) |
| France | 13 | |
| India | 1 | |
| Italy | 11 | |
| Japan | 1 | |
| Hungary | 7 | |
| Mexico | 1 | |
| New South Wales | 2 | |
| New Zealand | 1 | |
| Norway | 2 | |
| Rhodesia | 1 | |
| Russia | 4 | |
| Spain | 4 | |
| Switzerland | 4 | |
| Sweden | 2 | |
| Transvaal | 1 | |
|
United States |
112 | 112 (=) |
| Total | 221 | 265-350 ? |
While there are definitely a number more
patents than those listed in the Catalogue (see Canada, Germany, Great
Britain and the U.S. in the list above), the often quoted figure of Tesla having
received 700 or more patents appears to be excessive. Judging from the
available data, the actual figure probably lies somewhere around 325 worldwide.
[1] Dr. Nikola Tesla — Complete Patents
[2] Nikola Tesla Patent Collection
[3] Nikola Tesla — Collected German and American Patents
* Have some additional data for the 'Tesla Worldwide Patents List' ?
Please contact
the Tesla Wardenclyffe Project.
As for the "rotating brush wireless detector," you can read about this single terminal vacuum tube in Tesla's lecture "Experiments with Alternate Currents of High Potential and High Frequency." You can find this lecture in a number of books, but I recommend INVENTIONS RESEARCHES AND WRITINGS OF NIKOLA TESLA as the best source. The description appears pp. 226-230, with illustrations. The construction of the tube itself is very similar to the now popular "plasma globe" novelty item.
Tesla's last project, at least that which received a significant amount of press coverage between 1934 & 1941, was a particle beam projector. While he did make some statements about the transmission of power with this unique open-ended vacuum tube, it was intended for directing energy at a specific target and not for broadcasting.
I believe that you are thinking about an earlier project related to the application of alternating electrical currents to wireless telegraphy and the transmission of power. This drew much of Tesla's attention in the period generally between 1891 and 1912. In "The Future of the Wireless Art" which appeared in WIRELESS TELEGRAPHY & TELEPHONY, 1908, pp. 67-71, Tesla made the following statement regarding the Wardenclyffe project on which he was then working:
"As soon as completed, it will be possible for a business man in New York to dictate instructions, and have them instantly appear in type at his office in London or elsewhere. He will be able to call up, from his desk, and talk to any telephone subscriber on the globe, without any change whatever in the existing equipment. An inexpensive instrument, not bigger than a watch, will enable its bearer to hear anywhere, on sea or land, music or song, the speech of a political leader, the address of an eminent man of science, or the sermon of an eloquent clergyman, delivered in some other place, however distant. In the same manner any picture, character, drawing, or print can be transferred from one to another place. Millions of such instruments can be operated from but one plant of this kind. More important than this, however, will be the transmission of power, without wires, which will be shown on a scale large enough to carry conviction. These few indications will be sufficient to show that the wireless art offers greater possibilities than any invention or discovery heretofore made, and if the conditions are favorable, we can expect with certitude that in the next few years wonders will be wrought by its application."
If we can believe the above, an interesting feature of Tesla's World System for global communications, had it gone into full operation, would have been its capacity to provide small but usable quantities of electrical power at the location of the receiving circuits. He predicted that further advances would have permitted the wireless transmission of industrial amounts of electrical energy with minimal losses to any point on the earth's surface. If he had been able to complete the prototype communications station on Long Island and use it to demonstrate the feasibility of wireless power transmission than construction of a pilot plant for this larger system would have begun at Niagara Falls, site of the world's first commercial three phase AC power plant.
I hope this helps to answer your question. To learn more about this creative turn-of-the-century inventor visit your local library and ask about the intra-library loan system.
Nikola Tesla was born in Croatia of Serbian heritage. He is known to have said, "I am equally proud of my Serbian birth and Croatian Fatherland."
In 1884, literally within weeks of his arrival in New York City from Europe, Tesla went to work for Thomas Edison. One of his early assignments was the redesign of some machinery related to Edison's direct current power distribution system. Tesla's own words might best describe what happened next. "... I designed twenty-four different types of standard machines with short cores and of uniform pattern which replaced the old ones. The Manager had promised me fifty thousand dollars on the completion of this task but it turned out to be a practical joke. This gave me a painful shock and I resigned my position." You can read the complete account in Tesla's autobiography "My Inventions."
Nikola Tesla's disk turbine consists simply of multiple shaft mounted disks suspended upon bearings which position the rotor system within its cylindrical casing. In operation high velocity gases enter tangentially at the periphery of the disks, flow between them in free spiral paths to exit, depleted of energy, through central exhaust ports. The slight viscosity of the moving gas along with its molecular adhesion to the disks combine to drag them along, efficiently transferring the fuel's energy to the disks and on to the shaft.
There are some who believe that if this engine was built using advanced technology and materials it would have a power-to-weight ratio that compares favorably with bladed turbine engines. The U.S. Patents which covered the pump and the engine were issued in 1913 under the titles FLUID PROPULSION and TURBINE. Another related patent that describes a gas burning version of the disk turbine was issued in 1920 under the title VALVULAR CONDUIT.
There are a few books presently available where you can find the patents that I have mentioned above. One of these, "TESLA'S ENGINE -- A NEW DIMENSION FOR POWER, also contains a number of disk turbine related articles from Tesla's time, some in his own words.
Tesla obtained a number of
turbomachinery-related patents in the United States and abroad which serve as
primary sources of information on these devices. They
are included in the Nikola Tesla Patent Collection — On
CD-ROM
Nikola Tesla, Compiled by Bruce A. Perreault. The following books contain
additional useful information:
Dr. Nikola Tesla — Complete Patents
Nikola Tesla; Compiled by John T. Ratzlaff
Dr. Nikola Tesla — Selected Patent Wrappers
Nikola Tesla; Compiled by John T. Ratzlaff
The Tesla Bladeless Turbine and Related Turbomachinery
Nikola Tesla, et al; Compiled by Gary L. Peterson
Tesla's Engine — A New Dimension For Power
Nikola Tesla, et al; Compiled by Jeffery A. Hayes
Les Turbines a Frottements ou Turbines Tesla
(Frictional Turbines or Tesla Turbines)
Prof. E. Merigeault, free translation by Leland I. Anderson
Tesla Pump Comments
George Wiseman
Performance of Multiple-Disk-Rotor Pumps With Varied Interdisk Spacings
J.H. Morris
Laminar Flow Between Two Parallel Rotating Disks
M.C. Breiter & K. Pohlhausen
Tesla Turbine References Expanded Edition
Compiled by L.I. Anderson & W. Rice
There are also a number of Tesla Turbine related websites you may also wish to look into.
See also the entry Tesla turbine in the Wikipedia online encyclopedia.
The original Niagara Falls AC power plant, dubbed the Edward Dean Adams Hydro-Electric Power Station Number One, was designed to operate at a frequency of 25 cycles per second (Hz). A subsequent expansion of the Niagara Falls Power Company facility included a conversion to the now familiar 60 Hz. One other note, at the start of 1897 there were some 300 electrical power generating plants operating here in the U.S. The most important of these belonged to the Niagara Falls Power Company who transmitted 1000 horse power to Buffalo, New York on November 16, 1896. The current was used for the propulsion of electric street cars.
The small remote control boat that you read about (Tesla called it a telautomaton) was first demonstrated to the public in 1898 at New York City's Madison Square Garden. A patent with the long title "METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR CONTROLLING MECHANISM OF MOVING VESSELS OR VEHICLES, No. 613,809, was granted to Tesla the same year. His first demonstration of an apparatus for radio transmission and reception took place in 1893 during a lecture presentation in St. Louis before the National Electric Light Association. The entire lecture can be found in the book INVENTIONS, RESEARCHES AND WRITINGS OF NIKOLA TESLA.
The "fireball" account that you heard about can be traced back to the article "The New York Wizard of the West" which appeared in the May 1899 issue of Pearson's Magazine, London. Part of this article can be found on pages 3-4 of the Tesla biography titled TESLA MAN OUT OF TIME. Tesla himself discussed the production of fireballs or ball lightning in his "Colorado Springs Notes" (NIKOLA TESLA COLORADO SPRINGS NOTES 1899-1900) written at the time of his 1899 wireless propagation experiments.
While nothing could be found to indicate that Tesla had a residence in New Jersey, his first business venture, the Tesla Electric Light Company, was headquartered there in Rahway. It was formed in 1884 to satisfy a substantial market for electric-arc lights used to illuminate streets and factories. It is worthwhile noting that Tesla's first U.S. patent application dated March 30, 1885 was for an electric-arc lamp.
I have asked around and no one contacted has knowledge of Tesla ever having been tested for IQ. There is anecdotal evidence that even as a youth Tesla had a proclivity for problem solving, so I think it is fair to say that he was a truly gifted individual.
Many stories have been told of feats that Tesla is said to have performed which have no readily apparent basis in fact, and this could very well be one of them. On the other hand, the transmission of energy to achieve such a result might be accomplished with Tesla's particle-beam device—assuming the fundamental concept is valid. Considering statements made in a 1934 letter to the Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Co., Tesla certainly did. [See also the answer to Question 37.]
Of the myriad natural phenomena which manifest themselves in the universe, radio waves fall into the special category of things which cannot be directly observed. This helps to explain why they remained practically unknown until the 19th century when a number of important steps were taken by early investigators who developed techniques for their detection and measurement. This led to the 1886-88 experiments of Heinrich Hertz which firmly established their existence.
Nikola Tesla's contribution to all of this involved reworking the primitive radio frequency generators and tuned receiving circuits which his predecessors had developed. The first step was to introduce the coupled tuned circuit into the transmitter design. Some might recognize this as the configuration of the now familiar Tesla coil, with its primary and secondary circuits both tuned to vibrate in harmony with each other. Subsequent work resulted in the development of a receiver which also incorporated two synchronized circuits. Between 1898 and 1903 Tesla was granted 10 U.S. patents covering his work in these areas.
In 1904 Marconi was able to get his own patent using some of Tesla's ideas. The issue of patent infringement by Marconi was addressed in a lawsuit brought by Tesla 1915. Nothing significant resulted from this until 1916 when the Marconi Wireless Telegraph Company of America itself sued the United States for alleged damages resulting from the use of wireless during WWI. In 1943 the U.S. Supreme Court invalidated the fundamental Marconi patent because it was anticipated by Tesla. It is worthwhile noting that the following definition of radio was developed as a result of this case:
A radio communication system requires two tuned circuits each at the transmitter and receiver, all four tuned to the same frequency.
I would have to say that Tesla's best friend was Robert Underwood Johnson, editor of the Century Magazine and personal confidant. This is evident from the large volume of Johnson's correspondence that has been preserved at the Nikola Tesla Museum in Belgrade. As for his other "best friend," in Tesla's youth it was a cat named Macak. This animal is the subject of a charming short story related to a Miss Pola Fotitch in 1939. It can be found on page 283 of the book "Tesla Said" which also contains a large number of other significant accounts in Nikola Tesla's own words.
It is possible that Nikola Tesla is best known for his remarkable statements regarding the wireless transmission of electrical power. His first efforts towards this end started in 1891 and were intended to simply "disturb the electrical equilibrium in the nearby portions of the earth... to bring into operation in any way some instrument" with the object of producing effects locally and detecting them at a distance. By 1899 the electrical potential of his transmitter had increased to the point that more room was needed for the sake of safety. This and other considerations led him to temporarily shift his experiments to a location just outside of Colorado Springs.
It was at this Colorado "Experimental Station" that Tesla had some early success in wireless power transmission. In one of his demonstrations, photographs show that "a small incandescent lamp was lighted by means of a resonant circuit grounded on one end, all the energy being drawn through the earth" from the nearby transmitter. In 1907 he even went as far as to make the following statement.
... to make the little filament glow, the entire surface of the planet, two hundred million square miles, must be strongly electrified. This calls for peculiar electrical activities, hundreds of times greater than those involved in the lighting of an arc lamp through the human body [a more spectacular demonstration]. What impresses him most, however, is the knowledge that the little lamp will spring into the same brilliancy anywhere on the globe, there being no appreciable diminution of the effect with the increase of distance from the transmitter.
It is not clear that Tesla was referring to effects produced by his large Colorado transmitter. More likely he was writing of what could be done with an even bigger transmitter such as the one that he was trying to complete at Wardenclyffe in New York.
The following books will help you to learn more about Nikola Tesla's work in wireless communications and power transmission:
Nikola Tesla On His Work With Alternating Currents and Their Application to Wireless Telegraphy, Telephony and Transmission of Power, Leland Anderson, Ed., Sun Publishing, 1992.
Nikola Tesla Colorado Springs Notes 1899-1900, Aleksandar Marincic, Nikola Tesla Museum, 1978.
Tesla described this reciprocating device as a "mechanical oscillator." The basic design is rather simple, consisting of a stationary cylindrical housing and a floating internal piston. Motion is imparted to the piston by alternately applying a pressurized gas through inlet ports located near the ends of the cylinder. In operation the purely mechanical form of this machine will impart mechanical vibrations to any object to which it is attached.
One application of the device, spoken of by Tesla, is called "tele-geo-dynamics." In a paper written in 1939 he explained that these transmitters could "enable the attainment of many scientific and commercial results of inestimable value." He went on to say that "they offer the best means for prospecting, incomparably more economical and effective than any known heretofore, making possible the accurate and unmistakable location of oil, coal, sulphur, iron and other mineral deposits in the simplest, cheapest and least objectionable manner."
There are a number of sources for information about these oscillators and the principles resonance. These include Dr. Nikola Tesla - Complete Patents, Nikola Tesla's Earthquake Machine, and Nikola Tesla's Teleforce & Telegeodynamics Proposals.
Among his various pursuits Nikola Tesla had a lifelong involvement with the identification and harnessing of energy sources. His early dream of deriving electrical power from waterfalls and the vision's subsequent fulfillment at Niagara Falls and elsewhere is a classic example of this. In addition to falling water, he also recognized the energy potential of the wind, the sun and, perhaps most importantly, terrestrial heat - what is now referred to as geothermal energy. As his experience increased he became convinced that it should also be possible to obtain energy directly from the ambient medium. This can be seen from his words spoken during a lecture before the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, at Columbia College, N.Y., May 20, 1891.
We are whirling through endless space with an inconceivable speed, all around us everything is spinning, everything is moving, everywhere is energy. There must be some way of availing ourselves of this energy more directly.
By June 1900 in his article "The Problem of Increasing Human Energy" Tesla was able to report his first efforts to produce what he called a "self-acting engine." His design was inspired by the work in cryogenics conducted by Dewar and Linde which showed that it was possible to reach a very low temperature by transforming heat into mechanical work. The machine itself was based partly upon his reciprocating mechanical oscillator. While his expectations were high for a practical realization of the idea, circumstances were such that he turned away from the project in favor of more fertile ground.
A later reference to the tapping of a non-conventional energy source was published in the Brooklyn Eagle, July 10, 1932. In the article he said, "I have harnessed the cosmic rays and caused them to operate a motive device," though admitting, "the amount of power he was able to develop in the device was insignificant." The article can be found in "Solutions to Tesla's Secrets," pp. 95-97. It is possible this motor was related to the single wire/no wire motor demonstrated during his 1892 lecture in London. This lecture is in Inventions, Researches and Writings of Nikola Tesla pp. 233-235.
Recent speculations about Tesla's involvement in the Tunguska event have been fueled mainly by a few statements made some time ago in the New York Times. For example, on March 20, 1907 he spoke of "projecting wave-energy" and again on April 21, 1908 a reference is made to the "direct application of electrical waves without the use of aerial engines or other implements of destruction." This topic is expanded upon in the book Tesla's Fuelless Generator and Wireless Method.
The actions taken following Dr. Tesla's death on January 7, 1943 were conducted in an orderly and respectful fashion. According to those present at the time, Tesla's papers and other personal possessions were placed under the charge of the Office of Alien Property which issued a certificate of ownership to his nephew Sava Kosanovich. It being wartime and considering Tesla's involvement in remote detection and advanced weapons development, it is believed the material was thoroughly inspected for items that might have been important to national defense. The estate was consolidated at a Manhattan storage facility and in 1952 it was shipped off to Yugoslavia.
Assuming that the Philadelphia experiment actually took place, a possible connection with Tesla's work could be traced back to his 1883 rotating magnetic field concept and a later proposal for the electronic detection of U-boats found in an article entitled "Tesla's Views on Electricity and the War." It is possible that these concepts could have been incorporated into experiments designed to investigate the reduction of radar visibility of navel vessels.
Now, regarding the fabled "set for interplanetary communications," this gadget is spoken of in an unusual book titled "Return of the Dove," pp. 195, 205-208. It is said to be reproducible using design clues to be "found in the lectures which Tesla gave between the years of 1890 to 1896..."
Also called a "Peace Ray," the account refers to Tesla's particle beam invention, first written about in the New York Sun, July 10, 1934. The device, which was based upon a special type of open ended vacuum tube, comprised a system for the acceleration of very small charged metallic particles to high velocity. The particles were projected out of the tube by means of electro-static repulsion. As can be seen from Tesla's words written in a letter to J.P. Morgan, Jr. on November 29, 1934 it was intended for use in national defense.
I have made recent discoveries of inestimable value which are referred in the marked passage of the clipping enclosed... [possibly "Dr. Tesla Visions the End of Aircraft In War," "Syracuse Herald," October 21, 1934] The flying machine has completely demoralized the world, so much that in some cities, as London and Paris, people are in mortal fear from aerial bombing. The new means I have perfected afford absolute protection against this and other forms of attack.
The tube was designed to project a single row of highly charged minute metallic bodies. According to Tesla there would be no dispersion whatever, even at great distance. Since the cross section of the carriers might be reduced to almost microscopic dimensions, an immense concentration of energy, practically irrespective of distance, could be attained. [See also the answer to Question 28.]
Tesla's involvement in this area is best addressed in general terms. While there is no corroborated evidence that Tesla ever built an electric automobile, he is known to have encouraged others to pursue the idea of electric propulsion. He defined this as the use of an engine to generate electricity which was transmitted to an electric motor used to turn a wheel or propeller, instead of turning them by direct mechanical means. If this sounds familiar you're right, as the idea has recently seen a revival by the automobile industry and others under the name "hybrid electric drive."
The earliest reference to electric propulsion is found in the "Problem of Increasing Human Energy" where Tesla advocated the use of an "electric transmission" to drive ships and locomotives. Late in 1904 he extended this "view of future motive power" to include "the application of electricity to the propulsion of automobiles." There can be little doubt his best explanation of the principles involved and the rational behind their application appeared in the Feb. 25, 1917 edition of the New York Herald under the headline "Electric Drive for Battle Ships." The concept was adopted by the U.S. Navy, eventually including a variety of different size vessels from destroyer escort to battleship.
P.S. I always make people listen to my history of Tesla before I show them any tricks. Unfortunately, most people don't care about the history; they just want to see the "lightning". This is the reality, and that's why I'm asking for any "tricks". When I do tricks, the people get more interested and even listen for a few seconds.
I haven't been to the Griffith Observatory but understand from an associate in Burbank that your Tesla coil is an impressive one. As for novel demonstrations, while there are a number that have been mentioned in the literature most of them involve direct connection to the oscillator. They include such things as the luminosity of a fine wire on a dielectric plate, glow discharge between two rings, brush discharge between two parallel wires, brush discharge through a dielectric plate, rotating pinwheel, and the lighting of a vacuum tube between two plates. Most of these can be traced back to the lectures of 1891-93, in particular the "Experiments With Alternate Currents of High Potential and High Frequency" delivered by Tesla in 1892 before the Institution of Electric Engineers in London.
With an oscillator such as yours, it might be best to focus on those which can be performed without direct physical contact. While the lighting of a fluorescent tube is a tried and true standard, it is possible to greatly improve the performance of this demonstration by adding a tuned circuit that is adjusted to vibrate in harmony with transmitter. This typically consists of a single layer wire coil or solenoid with the upper end connected to a metal plate and the lower end connected to an earth ground. The tube is inserted into the ground lead. Fine tuning can be accomplished by adjusting the size of the elevated plate which can be made of aluminum foil suspended from a light weight wooden "T" shaped frame. As an alternative to the fluorescent, it is possible to light a small incandescent lamp by connecting it to a shorter secondary coil wrapped around the solenoid. If you really want to get tricky, connect a small DC permanent magnet motor to the secondary through a silicon diode bridge rectifier.
While the circuits described above are quite simple, the difficulty arises in getting them in tune with the transmitter. You might want to enlist a local amateur radio operator to assist you with this. I also recommend a booklet titled Tesla Oscillator and Fluorescent Tube Driver that covers this very subject. Another good source of information is the Tesla Coil Builders Association, 3 Amy Lane, Queensbury, NY 12804-9432.
Given his great capacity for original thought and ability to mentally visualize mechanisms in extreme detail, it's likely that Tesla was autistic. His solitary life style and single mindedness towards engagement in the creative act lend support to this conclusion. Visit " Autism & The Internet" or "It's The Wiring, Stupid" by Harvey Blume and Talk of the Nation, Strange Scientists for additional thoughts on this subject. [Answer revised on 10/06/2004. My thanks to those who provided their valuable input about this state of mind. -- Gary Peterson]
The "pit" that you heard about is probably a reference to the 120 foot deep well-like shaft that was positioned directly below the immense wooden tower which can be seen in many old photographs of the Wardenclyffe site. If the communications facility had been completed, it is this above ground structure that would have housed a set of large coils that would have been the principle transmitting and receiving elements. As for the well below the tower, it was excavated so that a radial array of iron pipes could be installed deep underground to serve as a connection between the oscillator and the earth. Tesla rigged up special machines that were used to push these pipes, one length after another, out into the soft Long Island subsoil.
After the second Wardenclyffe foreclosure took effect and Tesla lost the property, practically everything of value was stripped from the site for salvage. In light of this fact it is unlikely that any equipment remains in the now back-filled shaft. Recent bore-hole surveys reaching all the way down to the 120 foot level tend to support this conclusion.
While Tesla experimented with what he called "phosphorescent" lamps, it was French physicist Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel (1820-1891) who first conceived the idea of placing a fluorescent coating on the inner surface of a high voltage gas discharge tube. Tesla's investigations in the area of high-voltage RF power processing techniques did result in the very first high efficiency, high frequency lighting ballasts. His seminal lectures on the topic of high frequency lighting are, "Experiments With Alternate Currents of Very High Frequency and Their Application to Methods of Artificial Illumination," "Experiments with Alternating Currents of High Potential and High Frequency" and "On Light and Other High Frequency Phenomena" all to be found in the book Inventions, Researches and Writings of Nikola Tesla. It's interesting to note that the world's first commercial fluorescent lamps, introduced by the Westinghouse Electric Company at the 1939 Chicago World's Fair, were of the low-voltage 50-60 Hz hot cathode type still in common use today. Only since the late 1980s have more efficient high-frequency ballasts—some with great similarities to those developed by Tesla over 100 years ago—begun to gain wider acceptance.
 Tesla
built his first oscillator as a tool for studying high-frequency electrical
phenomena. He also constructed high-frequency electrical alternators for
the same purpose. When it comes to describing practical applications for
this type of electrical power supply, top on my list is high-frequency electric
lighting. Tesla's investigations in the area of high-voltage RF power
processing techniques resulted in the very first high-efficiency, high-frequency
lighting ballasts. He experimented with both fluorescent- and
incandescent-type lamps, as well as high-frequency arc lighting. Some of
the modern electronic fluorescent ballasts which first appeared in the late
1980s have great similarities to those he developed in the 1890s, the principal
difference being replacement of the mechanical switching mechanism with a
solid-state device.
Tesla
built his first oscillator as a tool for studying high-frequency electrical
phenomena. He also constructed high-frequency electrical alternators for
the same purpose. When it comes to describing practical applications for
this type of electrical power supply, top on my list is high-frequency electric
lighting. Tesla's investigations in the area of high-voltage RF power
processing techniques resulted in the very first high-efficiency, high-frequency
lighting ballasts. He experimented with both fluorescent- and
incandescent-type lamps, as well as high-frequency arc lighting. Some of
the modern electronic fluorescent ballasts which first appeared in the late
1980s have great similarities to those he developed in the 1890s, the principal
difference being replacement of the mechanical switching mechanism with a
solid-state device.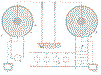 In
operating various devices with his high-frequency power supply using only one
connecting wire he realized the load can placed at some distance from the power
supply and still function properly. This is what Tesla called the
transmission of electrical energy through one wire without return.
Instead of using individual capacitor plates at the transmitting and receiving
ends, it is also possible to make a connection directly to the ground. In
this case the electrical circuit is completed entirely through the earth itself.
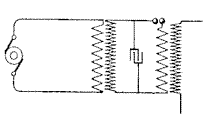
The accompanying illustration of a one-wire power transmission system is from
Tesla's U.S. Patent No. 593,138 titled ELECTRICAL TRANSFORMER, covering the
Tesla coil resonance transformer.
In
operating various devices with his high-frequency power supply using only one
connecting wire he realized the load can placed at some distance from the power
supply and still function properly. This is what Tesla called the
transmission of electrical energy through one wire without return.
Instead of using individual capacitor plates at the transmitting and receiving
ends, it is also possible to make a connection directly to the ground. In
this case the electrical circuit is completed entirely through the earth itself.
The accompanying illustration of a one-wire power transmission system is from
Tesla's U.S. Patent No. 593,138 titled ELECTRICAL TRANSFORMER, covering the
Tesla coil resonance transformer.
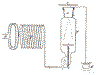 His
work with the single terminal incandescent lamp led him to investigate other
phenomena associated with vacuum tubes including the generation and physical
properties of X rays. Tesla was one of the first researchers to alert the
scientific community to some of the biological hazards associated with X-ray
exposure. Tesla's more advanced tubes differ from typical X-ray tubes in
that they have no target electrode and produce X rays through vacuum high-field
emission and a process known as Bremsstrahlung. His work in this area set
the stage for the development of high-energy particle accelerators. [Nikola
Tesla: Lecture Before The New York Academy of Sciences, April 6, 1897]
His
work with the single terminal incandescent lamp led him to investigate other
phenomena associated with vacuum tubes including the generation and physical
properties of X rays. Tesla was one of the first researchers to alert the
scientific community to some of the biological hazards associated with X-ray
exposure. Tesla's more advanced tubes differ from typical X-ray tubes in
that they have no target electrode and produce X rays through vacuum high-field
emission and a process known as Bremsstrahlung. His work in this area set
the stage for the development of high-energy particle accelerators. [Nikola
Tesla: Lecture Before The New York Academy of Sciences, April 6, 1897]
 When
standing in the same room as an operating Tesla coil, one might observe the
presence of the aromatic gas ozone. Tesla took advantage of this operating
characteristic by designing a device for the production of ozone in unlimited
amount (U.S. Pat. #568,177, Sept. 22, 1896). Tesla observed that with some
additional energy and certain modifications it is possible to efficiently induce
a reaction between oxygen and relatively inert nitrogen. In the industrial
processes for the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen, the resulting gaseous oxides
are reacted with other substances to form solid nitrogen compounds. [Dr.
Nikola Tesla — Complete Patents]
When
standing in the same room as an operating Tesla coil, one might observe the
presence of the aromatic gas ozone. Tesla took advantage of this operating
characteristic by designing a device for the production of ozone in unlimited
amount (U.S. Pat. #568,177, Sept. 22, 1896). Tesla observed that with some
additional energy and certain modifications it is possible to efficiently induce
a reaction between oxygen and relatively inert nitrogen. In the industrial
processes for the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen, the resulting gaseous oxides
are reacted with other substances to form solid nitrogen compounds. [Dr.
Nikola Tesla — Complete Patents]
 As
Tesla's research progressed, he placed additional emphasis on finding a solution
to one of the most vexing problems of his era—the
development of a practical system for wireless telegraphy and telephony.
Some preliminary experiments with high-frequency alternators connected to
an aerial and ground showed promising results towards this end. He next
replaced the alternator with his resonance transformer and achieved even better
results. When used as a radio transmitter it was demonstrated that Tesla's
oscillator, with its tuned primary and secondary circuits, was able to produce
radio waves thousands of times more powerful than the simple spark-coil
transmitter used by Heinrich Hertz just a few years before hand—a
practical application indeed! [Nikola Tesla On His Work With Alternating
Currents and Their Application to Wireless Telegraphy, Telephony, and
Transmission of Power]
As
Tesla's research progressed, he placed additional emphasis on finding a solution
to one of the most vexing problems of his era—the
development of a practical system for wireless telegraphy and telephony.
Some preliminary experiments with high-frequency alternators connected to
an aerial and ground showed promising results towards this end. He next
replaced the alternator with his resonance transformer and achieved even better
results. When used as a radio transmitter it was demonstrated that Tesla's
oscillator, with its tuned primary and secondary circuits, was able to produce
radio waves thousands of times more powerful than the simple spark-coil
transmitter used by Heinrich Hertz just a few years before hand—a
practical application indeed! [Nikola Tesla On His Work With Alternating
Currents and Their Application to Wireless Telegraphy, Telephony, and
Transmission of Power]
 In
spite of this initial success Tesla was clearly not satisfied with his results.
Further improvements included the development of techniques for obtaining
frequency stability, selectivity, immunity to interference, and security of
communications. It is a footnote to history that a portion of this work
with high-power radio-frequency oscillators involved the first electronic
implementation of the AND logic function. The resulting U.S. Patents #
723,188 & # 725,605 for wireless signaling cover logic gates in general and
also describe the basic principles of frequency-hopping and frequency-division
multiplexing in wireless spread spectrum telecommunications. See Wireless
Remote Control and the Electronic Computer Logic Gate for an exhibit in the U.S.
patent interference "Nikola Tesla vs. Reginald A. Fessenden, Interference
No. 21,701, Systems of Signaling" showing a circuit diagram of an
electronic AND logic gate used by Tesla in 1899. [Nikola Tesla: Guided
Weapons & Computer Technology]
In
spite of this initial success Tesla was clearly not satisfied with his results.
Further improvements included the development of techniques for obtaining
frequency stability, selectivity, immunity to interference, and security of
communications. It is a footnote to history that a portion of this work
with high-power radio-frequency oscillators involved the first electronic
implementation of the AND logic function. The resulting U.S. Patents #
723,188 & # 725,605 for wireless signaling cover logic gates in general and
also describe the basic principles of frequency-hopping and frequency-division
multiplexing in wireless spread spectrum telecommunications. See Wireless
Remote Control and the Electronic Computer Logic Gate for an exhibit in the U.S.
patent interference "Nikola Tesla vs. Reginald A. Fessenden, Interference
No. 21,701, Systems of Signaling" showing a circuit diagram of an
electronic AND logic gate used by Tesla in 1899. [Nikola Tesla: Guided
Weapons & Computer Technology]
While many of Tesla's innovations are embodied in our present apparatus for
wireless telecommunications there are certain elements which have not been
incorporated. In Tesla's own words, "devices of this kind, to be most
effective and efficient, should be designed with due regard to the physical
properties of this planet and the electrical conditions obtaining on the
same." [The
True Wireless]

All rights reserved, 1998-2005
Gary Peterson